Major U.S. indices pushed to fresh record highs this week even as labor market data showed concerning signs of weakness. The Dow Jones Industrial Average, S&P 500 and Nasdaq Composite all touched new peaks during the same period that initial jobless claims jumped to 263,000, their highest level since October 2021. The unemployment rate now sits at 4.3%, a development that’s getting more attention from both markets and policymakers. Perhaps most concerning is the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ preliminary benchmark revision, which revealed the U.S. economy created 911,000 fewer jobs than previously reported during the 12 months ending in March 2025. This suggests the labor market has been weaker for longer than many realized and could push the Fed to act more decisively than markets currently expect.
The inflation picture remains mixed and creates a complex backdrop for Fed policy. The CPI accelerated to 2.9% year-over-year in August, up from July’s 2.7% reading, while producer price inflation unexpectedly cooled to 2.6% from the previous month’s 3.1%. Core inflation measures continue to show persistent underlying price pressures, with core CPI holding steady at 3.1% year-over-year for the second consecutive month. Food costs showed concerning momentum with grocery prices rising 0.5% in August, the sharpest monthly increase in nearly three years. The divergent readings between headline and producer inflation may not change the Fed’s likely path in September, but the question for investors is whether the uptick in CPI represents a temporary deviation or the beginning of a more concerning trend.
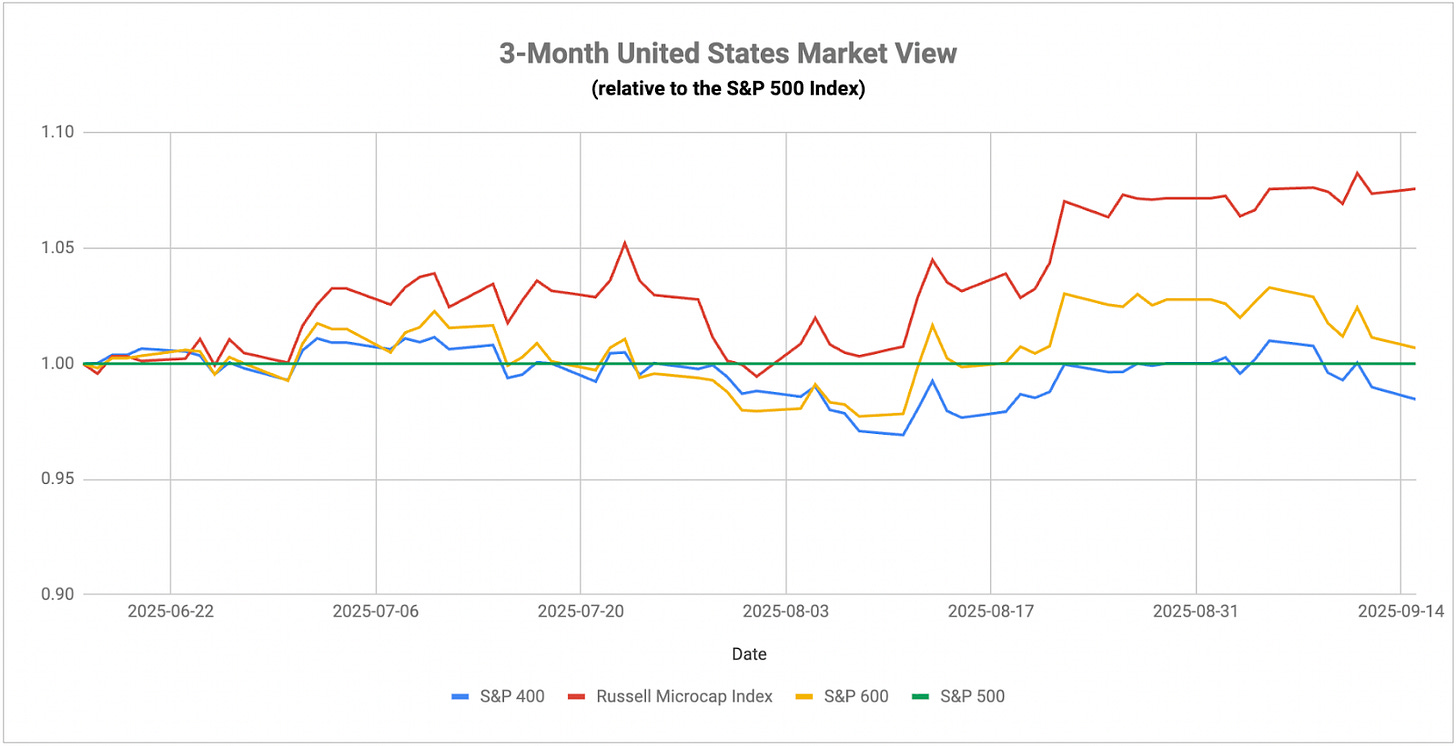
The equity market’s resilience in the face of deteriorating economic data has been driven largely by two forces: artificial intelligence enthusiasm and anticipation of Fed policy easing. Technology and AI-linked stocks continue to power Wall Street’s main indexes higher with the communications services sector jumping more than 20% year-to-date. Oracle’s performance last week provided a perfect example of this dynamic with shares surging 36% in a single session after reporting multibillion-dollar AI contracts with OpenAI. The eight most valuable AI-related companies in the U.S. stock market now constitute almost 30% of the S&P 500, creating both opportunity and risk. The question becomes whether this AI-driven momentum can sustain itself if the broader economic backdrop continues to weaken.
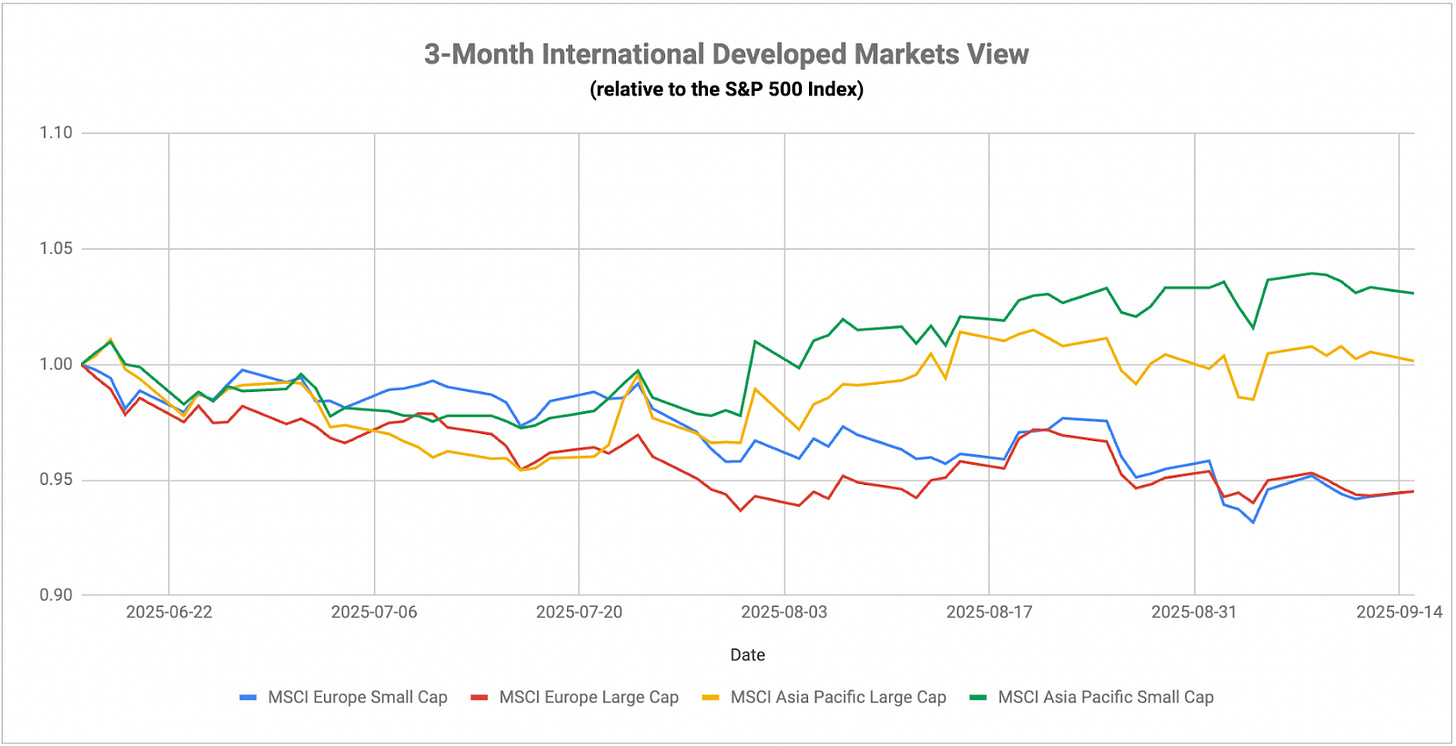
The European Central Bank maintained its benchmark rate unchanged on Thursday, keeping policy steady while inflation remains close to the 2% target. ECB President Christine Lagarde struck a confident tone during her press conference, declaring that “the disinflationary process is over” and emphasizing that the Eurozone remains “in a good place” with inflation at 2.1%. The central bank’s updated projections show minor adjustments to the inflation path ahead with headline inflation now expected to average 2.1% in 2025 and 1.7% in 2026, both revised up by 0.1 percentage points from June’s forecast. Market expectations shifted following the meeting with traders now seeing just under a 50% chance of another ECB rate cut by June 2026, down from around 60% before the decision.